English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català שפה עברית
שפה עברית Cymraeg
Cymraeg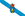 Galego
Galego Latviešu
Latviešu icelandic
icelandic ייִדיש
ייִדיש беларускі
беларускі Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra Հայերեն
Հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba অসমীয়া
অসমীয়া ଓଡିଆ
ଓଡିଆ Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türkçe
Türkçe Gaeilge
Gaeilge العربية
العربية Indonesia
Indonesia Norsk
Norsk تمل
تمل český
český ελληνικά
ελληνικά український
український Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақша
Қазақша Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Srpski језик
Srpski језик
Quangong Brick Making Laboratory Achieves New Breakthrough in Co-utilization of Multi-Source Solid Waste
2025-12-22
Quanzhou Gong Machinery Co., Ltd. continues to deeply cultivate the field of solid waste resource utilization and constantly explores green building material equipment and process innovation. Recently, Quanzhou Gong's brick-making laboratory has achieved phased results in the research of solid waste brick-making technology. It has successfully completed the standard brick preparation experiment using three types of solid waste—incineration ash, phosphorus slag, and coal gangue—as the main raw materials, providing a feasible path for the high-value utilization of multi-source solid waste.
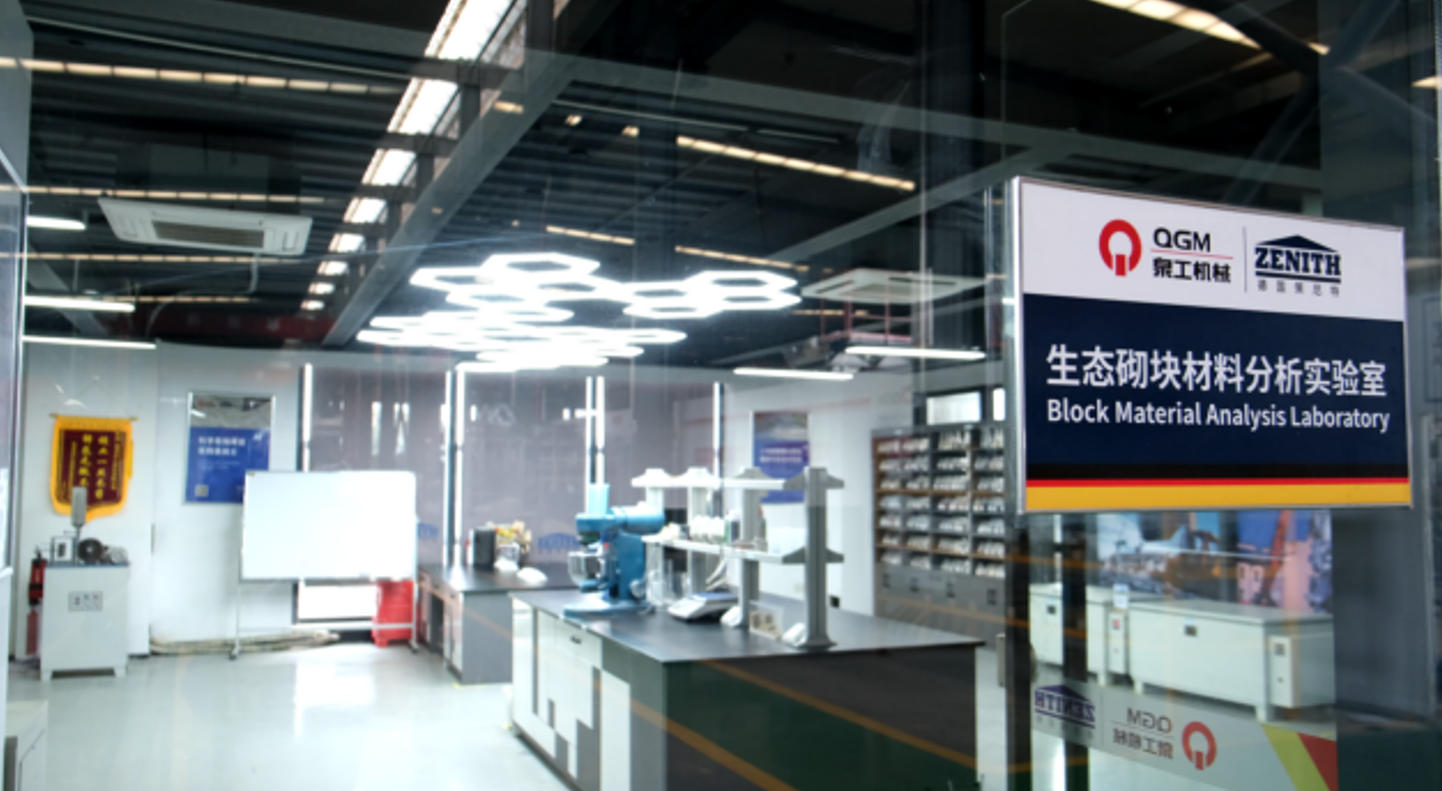

Incineration ash, phosphorus slag, and coal gangue are widely sourced and have complex compositions, facing significant challenges in their treatment and disposal for a long time. Quanzhou Gong brick-making laboratory, relying on comprehensive testing facilities and a professional technical team, conducted component analysis and proportion optimization of these three solid wastes. Combining the physical properties and chemical reactivity of different materials, it developed targeted brick-making process solutions. During the experiments, the laboratory used mature and reliable brick-making equipment for molding tests. Through multiple rounds of parameter adjustments and process verification, it successfully produced standard non-fired bricks that met the requirements for strength, size, and appearance.
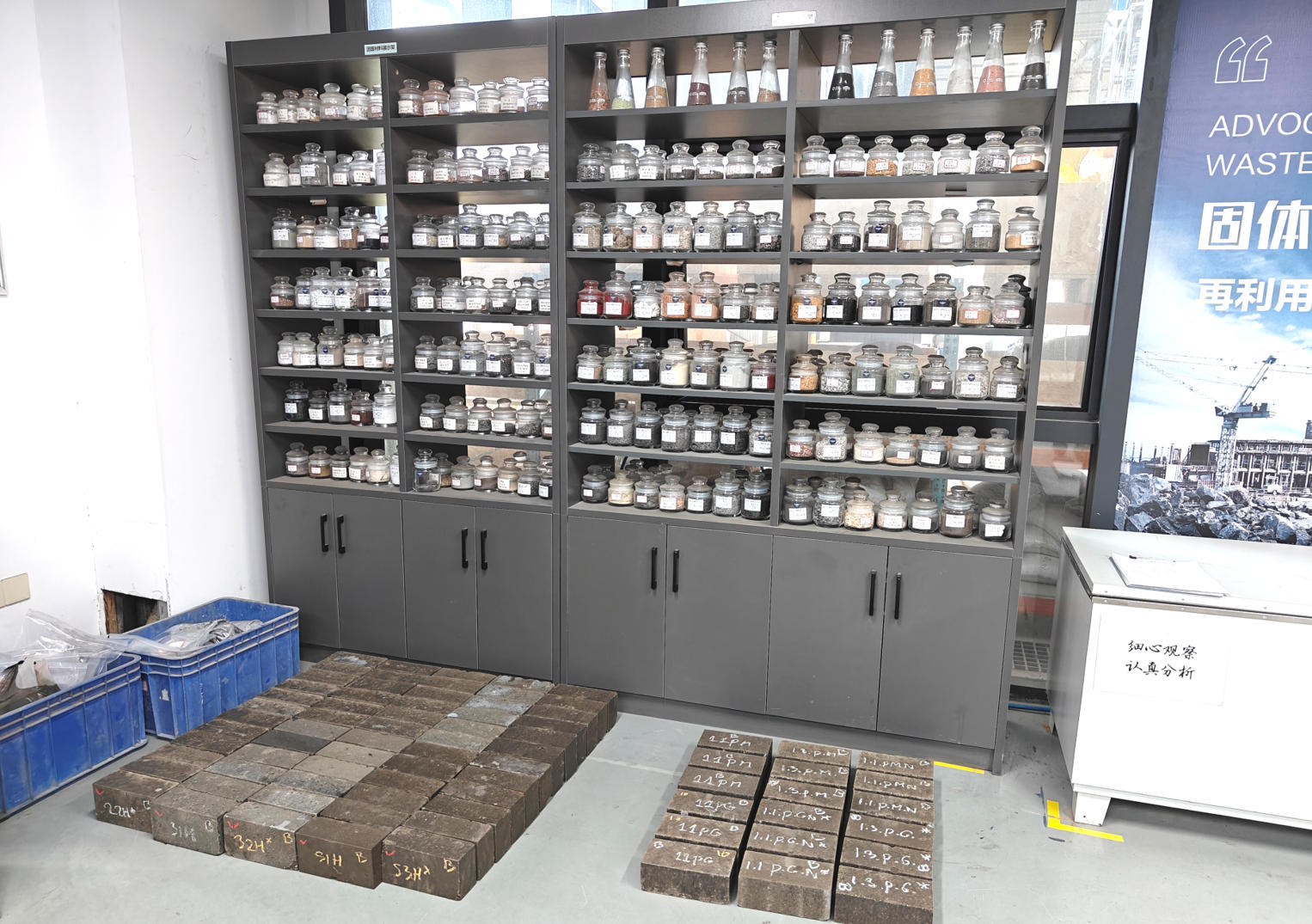

This experimental result not only verifies the feasibility of co-processing bricks from multiple solid wastes, but also further demonstrates the technological advantages of non-fired brick machines in the resource utilization of solid waste. Through the non-fired molding process, solid waste can be transformed into stable block products without high-temperature calcination, effectively reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions, aligning with the current trend of green building materials development under the "dual carbon" background. This technological breakthrough marks a solid step forward for Quanzhou Machinery in the field of co-processing and high-value utilization of complex multi-source solid waste, providing a more universal and economical innovative solution for the construction of "zero-waste cities."